In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have found a new use for ocean bacteria in battling climate change.
They have bolstered the bacteria's ability to capture and store carbon in the ocean, mitigating harmful greenhouse gas emissions.
Marine microorganisms, namely cyanobacteria, have been modified so that they can soak up CO2, the primary culprit driving global climate change.
The bacterium used, Prochlorococcus, is one of the most abundant photosynthetic organisms on the planet and is responsible for a significant portion of photosynthesis on Earth.
The re-engineered bacteria can absorb more CO2 even in conditions where there's less of the gas, and they store the carbon in their bodies instead of releasing it back into the environment.
This innovative line of research offers a unique approach to tackling excessive greenhouse gases in our atmosphere.
While more work is needed to ensure the safety and efficacy of this method, the preliminary findings offer a tantalising possibility in the combat against climate change. It also highlights the critical role nature can play in mitigating environmental issues.
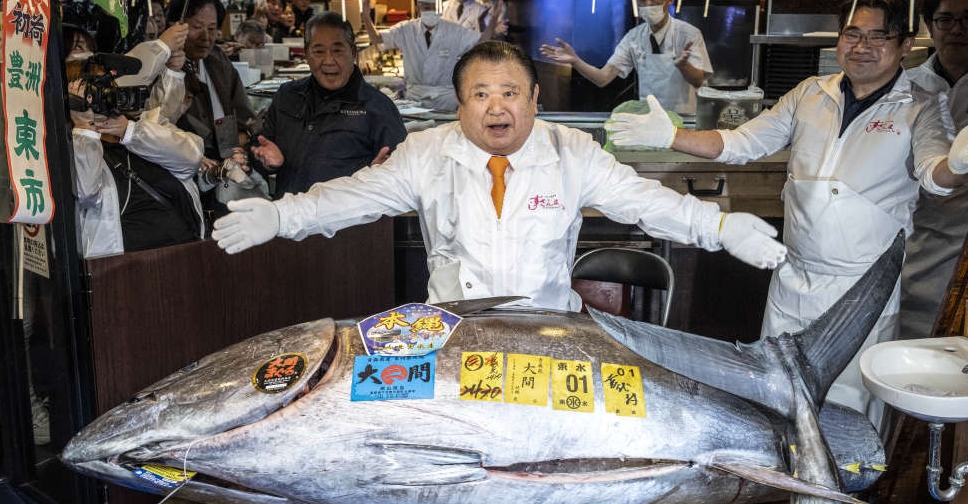




 Popular Japanese sushi chain pays record $3.2 million for tuna in New Year auction
Popular Japanese sushi chain pays record $3.2 million for tuna in New Year auction
 Thousands of dinosaur footprints found near Winter Olympics site
Thousands of dinosaur footprints found near Winter Olympics site
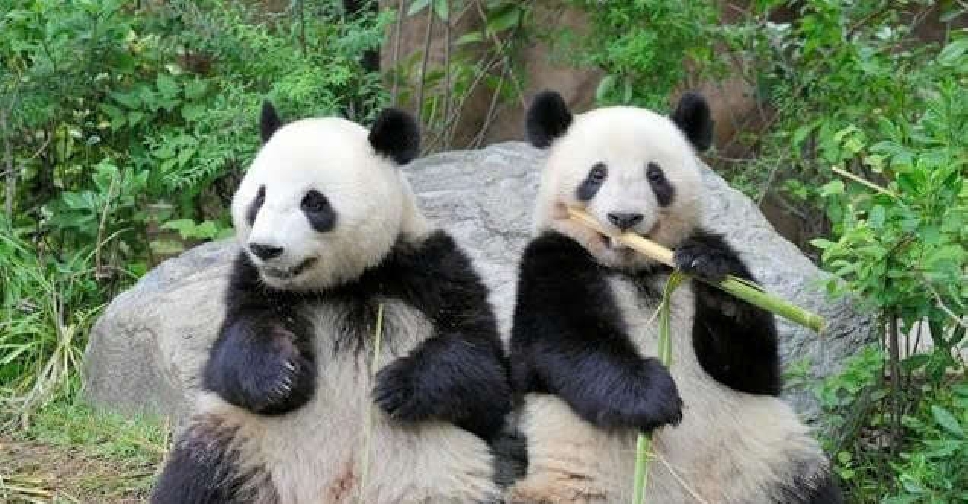 Japan's last two giant pandas are headed to China and fans just can't bear it
Japan's last two giant pandas are headed to China and fans just can't bear it
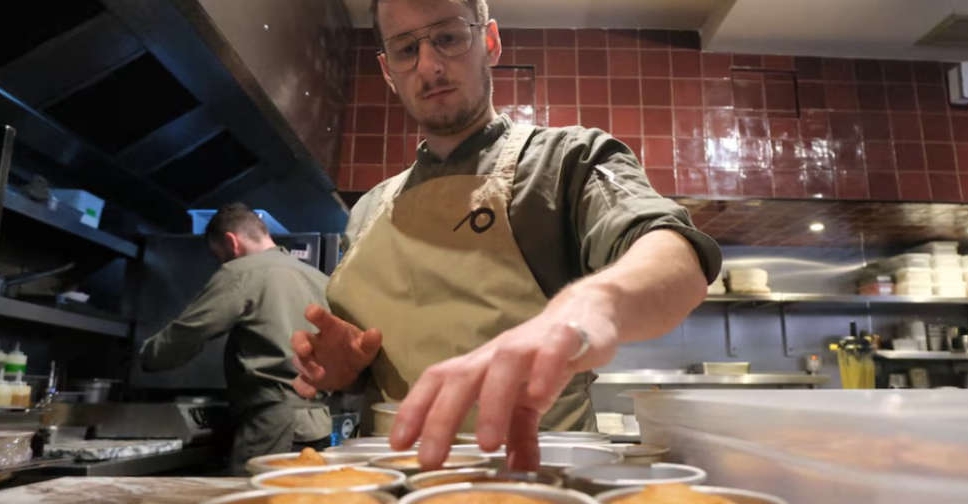 At Britain's first plant-based Michelin-star restaurant, most diners aren't vegan
At Britain's first plant-based Michelin-star restaurant, most diners aren't vegan
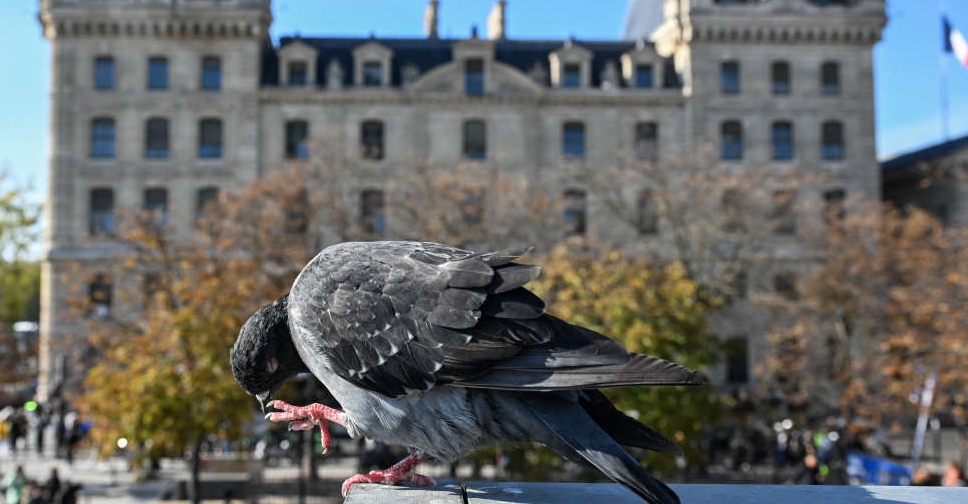 'No strings attached': Meet Paris' pigeon doctor
'No strings attached': Meet Paris' pigeon doctor

